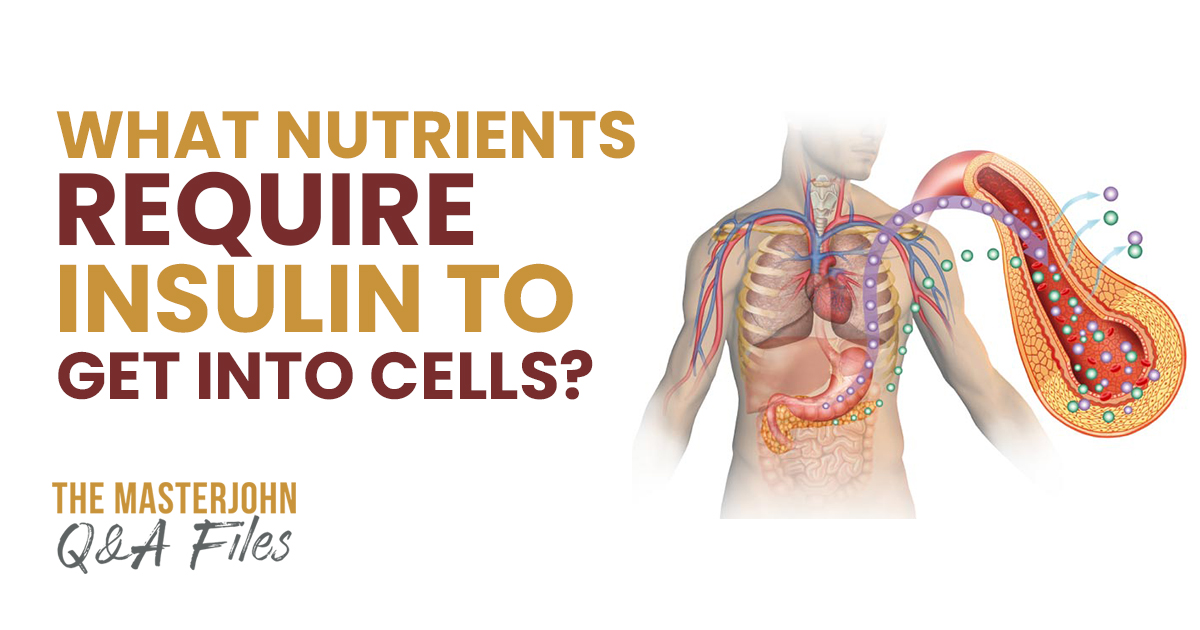
Please consider supporting my work by making a purchase using these links at one of my affiliates: https://chrismasterjohnphd.com/foursigmatic, https://chrismasterjohnphd.com/paleovalley, https://chrismasterjohnphd.com/seekinghealth, https://chrismasterjohnphd.com/ancestralsupplements, https://chrismasterjohnphd.com/magicspoon, https://chrismasterjohnphd.com/lmnt Plenty more at https://chrismasterjohnphd.com/support! Question: What nutrients require insulin to get into cells? Magnesium phosphorus and potassium are the big ones that are going to have poor uptake in response to insulin. …